Maintaining balanced blood sugar levels is essential for sustained energy, metabolic health, and long-term disease prevention. While many beverages contribute to sudden glucose spikes, coconut water stands out as a natural option that may help support blood sugar balance when consumed mindfully.
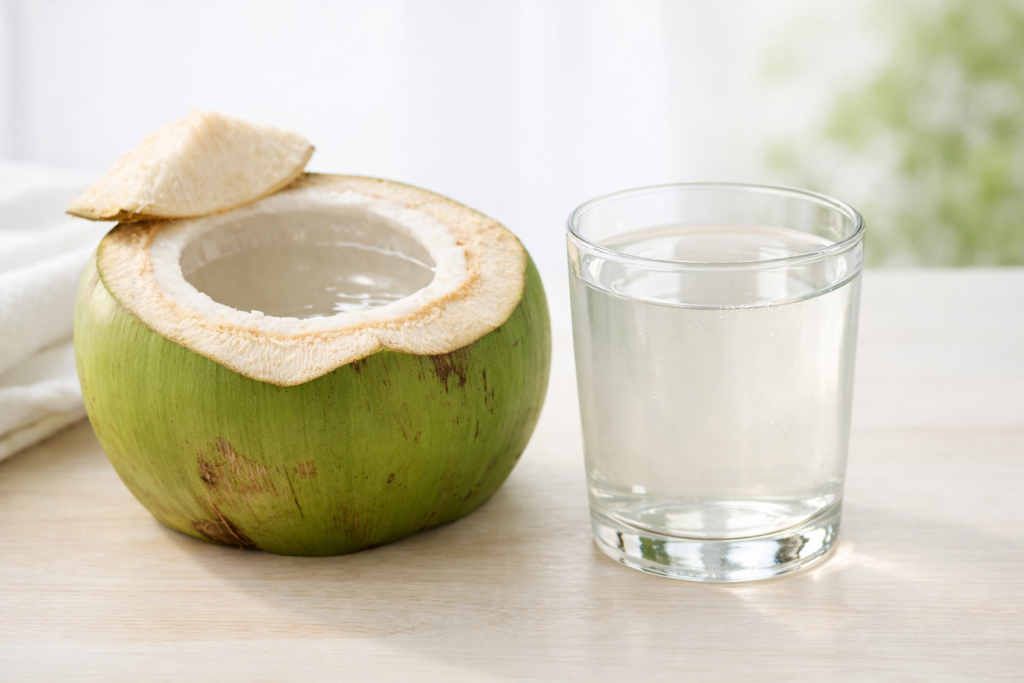
Derived from young green coconuts, coconut water is not just refreshing—it contains essential electrolytes, trace minerals, and bioactive compounds that can positively influence glucose metabolism.
Why Blood Sugar Balance Matters
Blood sugar fluctuations occur when glucose enters the bloodstream faster than insulin can regulate it. Repeated spikes may lead to:
- Insulin resistance
- Increased hunger and cravings
- Fatigue and mood swings
- Higher risk of type 2 diabetes
Choosing beverages with low sugar load, proper hydration capacity, and mineral support can help maintain steady glucose levels throughout the day.
Coconut Water: A Functional Beverage, Not Just a Drink
Unlike sweetened juices or sodas, natural coconut water is:
- Low in calories
- Free from refined sugar
- Rich in potassium and magnesium
- Naturally hydrating
- Lightly sweet with a low glycemic impact (in small servings)
This makes it particularly relevant for people aiming to reduce sugar intake without sacrificing taste or hydration.
How Coconut Water May Help Regulate Blood Sugar
1. Supports Insulin Function Through Essential Minerals
Coconut water contains magnesium and potassium, both of which are crucial for insulin activity. Magnesium helps improve insulin sensitivity, allowing glucose to move efficiently from the blood into cells.
Low magnesium levels have been associated with impaired glucose control, making coconut water a supportive addition to a balanced diet.
2. Helps Prevent Dehydration-Related Sugar Spikes
Even mild dehydration can increase blood sugar concentration. Coconut water replenishes fluids while restoring electrolytes, helping the body maintain optimal glucose circulation and utilization.
This benefit is especially important in hot climates, during fasting periods, or after physical exertion.
3. Provides Natural Sugars in Controlled Amounts
Coconut water contains natural sugars, but in far smaller quantities than packaged juices. When consumed in moderation, it delivers steady energy without overwhelming the bloodstream with glucose.
Unlike refined sugar, these natural carbohydrates are accompanied by minerals that assist metabolic processing.
4. Antioxidants May Reduce Insulin Resistance
Oxidative stress plays a role in insulin resistance and metabolic disorders. Coconut water contains antioxidants that help neutralize free radicals, supporting healthier cellular function and glucose regulation over time.
5. May Reduce Dependence on High-Sugar Beverages
Replacing sugary drinks with coconut water can significantly lower overall sugar intake. This substitution alone may help stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce long-term metabolic strain.
Coconut Water for People with Diabetes: What to Know
Coconut water is not a free-drink for diabetics—but it can be included safely with proper portion control.
Safe Consumption Guidelines:
- Limit to 100–200 ml per serving
- Choose fresh coconut water, not packaged
- Avoid drinking alongside high-carb meals
- Best consumed mid-morning or post-exercise
- Monitor blood sugar response individually
Packaged coconut waters often contain added sugars and should be avoided.
Best Time to Drink Coconut Water for Glucose Stability
- Morning (after waking) – Supports hydration and mineral balance
- After physical activity – Replenishes electrolytes without refined sugar
- Midday – Helps prevent energy crashes and sugar cravings
Avoid late-night consumption, especially for those sensitive to glucose fluctuations.
Fresh Coconut Water vs Processed Versions
| Fresh Coconut Water | Packaged Coconut Water |
|---|---|
| Naturally low sugar | Often sweetened |
| Rich in enzymes | Nutrient loss during processing |
| Better glycemic response | Higher sugar load |
| Ideal for blood sugar | Less suitable for diabetics |
Fresh is always the superior option.
Who Should Limit or Avoid Coconut Water?
- People with advanced diabetes
- Individuals with kidney disease (high potassium)
- Those on potassium-restricted diets
Medical guidance is recommended in these cases.
Final Verdict
Coconut water can be a supportive beverage for blood sugar balance when consumed in moderation and as part of a nutrient-dense diet. Its hydration benefits, mineral content, and low glycemic impact make it a smarter alternative to sugary drinks—but portion control remains key.
It is not a treatment for diabetes, yet it can complement a healthy lifestyle aimed at stable glucose levels.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can coconut water raise blood sugar levels?
Coconut water contains natural sugars, so drinking it in large amounts may increase blood sugar levels. However, when consumed in moderation, fresh coconut water generally has a low glycemic impact and is less likely to cause sudden glucose spikes.
Is coconut water safe for people with diabetes?
Yes, people with diabetes can include coconut water in their diet if consumed carefully. Choosing fresh, unsweetened coconut water and limiting the portion size helps reduce the risk of blood sugar fluctuations.
Why is coconut water better than sugary drinks for blood sugar balance?
Coconut water provides hydration along with essential minerals like potassium and magnesium, which support insulin function. Sugary drinks lack these nutrients and often cause rapid blood sugar spikes.
How much coconut water should be consumed for blood sugar support?
For most people, consuming 100–200 ml of coconut water per day is sufficient. Drinking more than this regularly may increase sugar intake, especially for individuals with insulin resistance.
What is the best time to drink coconut water for stable glucose levels?
Coconut water is best consumed in the morning, after physical activity, or during midday hours. These times help maximize hydration benefits without significantly affecting blood sugar levels.
Is fresh coconut water better than packaged coconut water?
Fresh coconut water is the healthier option because it contains no added sugars or preservatives. Packaged versions may have a higher glycemic load due to processing and sweeteners.